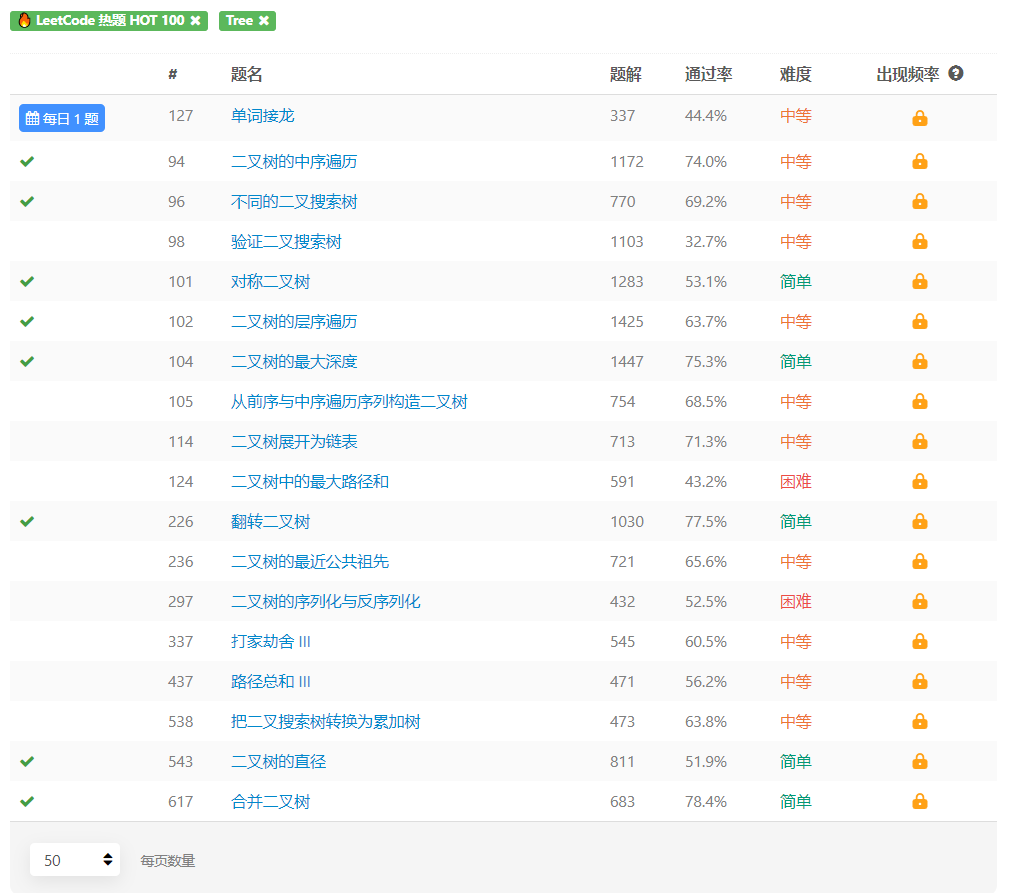
LeetCode-Tree
Free Talk
终于可以刷最常用的二叉树了,我对于二叉树的递归和迭代理解的不是很清楚,趁这篇文章学习总结一下。
Finished Problem
验证二叉搜索树
递归
1 | /** |
执行结果

中序遍历
1 | /** |
执行结果

从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
递归 (根节点 + 左右子树)
1 | /** |
执行结果
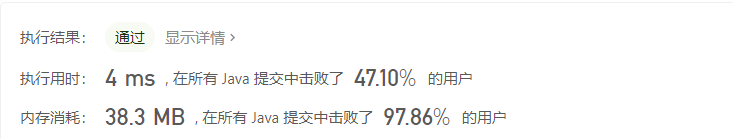
哈希表优化
1 | /** |
执行结果
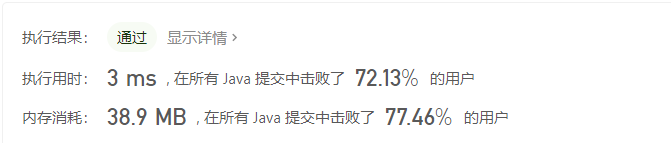
二叉树展开为链表
前序遍历
1 | /** |
执行结果

二叉树中的最大路径和
根据字符出现频率排序
桶排序
1 | class Solution { |
执行结果

二叉树的右视图
层序遍历 + 队列 + 输出最后一个元素
1 | /** |
执行结果

DFS + 深度判断
1 | // 在面试的过程中,使用的界面就相当于记事本,需要自己去写函数和类 |
执行结果

二叉树的最近公共祖先
后序遍历
1 | /** |
执行结果

打家劫舍 III
层序遍历(错误解法)
1 | /** |
DFS+哈希表
1 | /** |
执行结果

路径总和 III
前缀和
1 | /** |
执行结果

双重递归
1 | /** |
执行结果

把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
DFS + 右根左
1 | /** |
执行结果
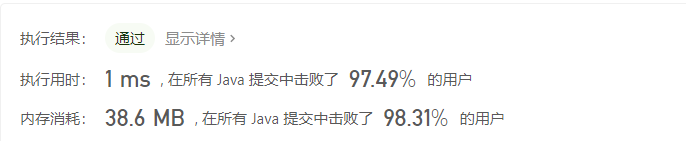
第一目标完成
自己刷了十几题的树,发现所有的题其实都是遍历问题,要学会把握遍历的顺序(根,左,右 间的次序交换)。
但是自己离十五分钟内,做出中等难度的算法题的目标,还相差甚远。因此打算另开一张,继续接着刷树类型,及其他高频的算法题。